封装二叉搜索树
二叉搜索树方法
插入方法:
- insert(value):向树中插入一个新的数据
查找方法:
- search(value):在树中查找一个数据,如果节点存在,则返回 true;如果不存在,则返回 false
- min:返回树中最小的值/数据
- max:返回树中最大的值/数据
遍历方法:
- inOrderTraverse:通过中序遍历方式遍历所有节点
- preOrderTraverse:通过先序遍历方式遍历所有节点
- postOrderTraverse:通过后序遍历方式遍历所有节点
- levelOrderTraverse:通过层序遍历方式遍历所有节点
删除方法:
- remove(value):从树中移除某个数据
插入数据
- 插入其他节点时,我们需要判断该值到底是插入到左边还是插入到右边
- 判断的依据来自于新节点的 value 和原来节点的 value 值的比较
- 如果新节点的 newValue 小于原节点的 oldValue,那么就向左边插入
- 如果新节点的 newValue 大于原节点的 oldValue,那么就向右插入
- 代码1位置,就是准备向左子树插入数据,但是它本身有分成两种情况
- 情况一:左子树上原来没有内容,那么直接插入即可
- 情况二:左子树上已经有了内容,那么久一次向下继续查找新的走向,所以使用递归调用即可
- 代码2位置,和代码1位置几乎逻辑是相同的,只是去向右查找
- 情况一:左右树上原来没有内容,那么直接插入即可
- 情况二:右子树上已经有了内容,那么就一次向下继续查找新的走向,所以使用递归调用即可
typescript
class BSTree<T> {
private insertNode(node: TreeNode<T>, newNode: TreeNode<T>) {
// 代码1
if (newNode.value < node.value) {
// 去左边继续查找空白位置
if (node.left === null) {
node.left = newNode
} else {
this.insertNode(node.left, newNode)
}
// 代码2
} else {
// 去右边继续查找空白位置
if (node.right === null) {
node.right = newNode
} else {
this.insertNode(node.right, newNode)
}
}
}
}遍历数据
- 遍历一棵树是指访问树的每个节点(也可以对每个节点进行某些操作,我们这里就是简单的打印)
- 但是树和线性结构不太一样,线性结构我们通常按照从前到后的顺序遍历,但是树呢?
- 应该从树的顶端还是底端开始呢?从左开始还是从右开始呢?
二叉树遍历常见的四种方式:
- 先序遍历
- 中序遍历
- 后序遍历
- 层序遍历

先序/中序/后序:取决于访问根节点(root)的时机
- 在所有的树结构中(包括子树)都是如此
先序遍历
- 优先访问根节点
- 之后访问左子树
- 最后访问右子树

- 递归版本
typescript
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
preOrderTraverse() {
this.preOrderTraverseNode(this.root)
}
private preOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
console.log(node.value)
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.left)
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.right)
}
}
}- 非递归版本
typescript
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
preOrderTraversalNoRecursion() {
let stack: TreeNode<T>[] = []
let current: TreeNode<T> | null = this.root
while (current !== null || stack.length !== 0) {
while (current !== null) {
console.log(current.value)
stack.push(current)
current = current.left
}
current = stack.pop()!
current = current.right
}
}
}中序遍历
- 优先访问左子树
- 之后访问根节点
- 最后访问右子树

- 递归版本
typescript
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
inOrderTraverse() {
this.inOrderTraverseNode(this.root)
}
private inOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
this.inOrderTraverseNode(node.left)
console.log(node.value)
this.inOrderTraverseNode(node.right)
}
}
}- 非递归版本
typescript
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
inOrderTraversalNoRecursion() {
let stack: TreeNode<T>[] = []
let current: TreeNode<T> | null = this.root
while (current !== null || stack.length !== 0) {
while (current !== null) {
stack.push(current)
current = current.left
}
current = stack.pop()!
console.log(current.value)
current = current.right
}
}
}后序遍历
- 优先访问左子树
- 之后访问右子树
- 最后访问根节点

- 递归版本
typescript
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
postOrderTraverse() {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(this.root)
}
private postOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(node.left)
this.postOrderTraverseNode(node.right)
console.log(node.value)
}
}
}- 非递归版本
typescript
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
preOrderTraversalNoRecursion() {
let stack: TreeNode<T>[] = []
let current: TreeNode<T> | null = this.root
while (current !== null || stack.length !== 0) {
while (current !== null) {
console.log(current.value)
current = current.left
}
current = stack.pop()!
stack.push(current)
current = current.right
}
}
}层序遍历
层序遍历很好理解,就是从上向下逐层遍历
层序遍历通常我们会借助队列来完成
- 也是队列的一个经典应用场景

typescript
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
levelOrderTraverse() {
// 1.如果没有根节点,那么不需要遍历
if (!this.root) return
// 2.创建队列结构
const queue: TreeNode<T>[] = []
queue.push(this.root)
// 3.遍历队列中所有的节点(依次出队)
while (queue.length) {
// 3.1.访问节点的过程
const current = queue.shift()!
console.log(current.value)
// 3.2.将左子节点放入队列
if (current.left) {
queue.push(current.left)
}
// 3.3.将右子节点放入到队列
if (current.right) {
queue.push(current.right)
}
}
}
}最值
在二叉搜索树中搜索最值是一件非常简单的事情,其实用眼睛就可以看出来了
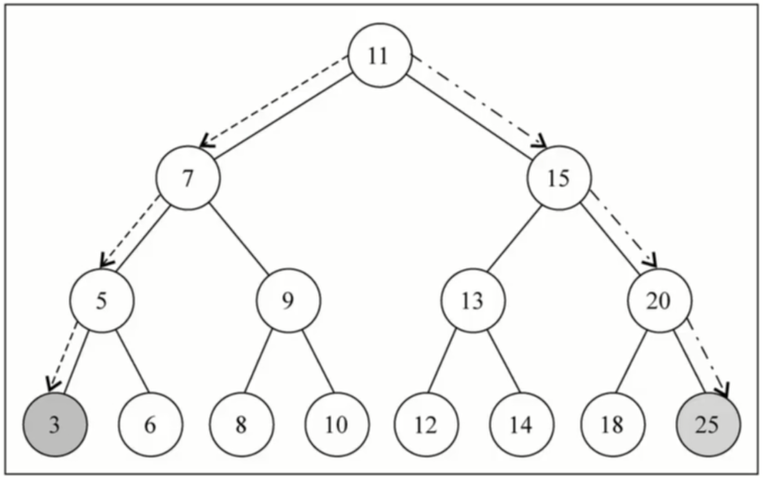
typescript
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
/** 获取最值操作:最大值 */
getMaxValue(): T | null {
let current = this.root
while (current && current.right) {
current = current.right
}
return current?.value ?? null
}
/** 获取最值操作:最小值 */
getMinValue(): T | null {
let current = this.root
while (current && current.left) {
current = current.left
}
return current?.value ?? null
}
}搜索特定的值
二叉搜索树不仅仅获取最值效率非常高,搜索特定的值效率也非常高
- 注意:这里的实现返回 boolean 类型即可
typescript
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
searchNoRecursion(value: T): boolean {
let current = this.root
while (current) {
// 找到了节点
if (current.value === value) return true
if (current.value < value) {
current = current.right
} else {
current = current.left
}
}
return false
}
search(value: T): boolean {
return this, this.searchNode(this.root, value)
}
searchNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null, value: T): boolean {
// 1.如果节点为null,那么就直接退出递归
if (node === null) return false
// 2.判断node节点的value和传入的value的大小
if (node.value > value) {
return this.searchNode(node.left, value)
} else if (node.value < value) {
return this.searchNode(node.right, value)
} else {
return true
}
}
}删除操作
二叉搜索树的删除有些复杂,我们一点点完成
删除节点要从查找到删除的节点开始,找到节点后,需要考虑三种情况:
- 该节点是叶节点(没有子节点,比较简单)
- 该节点有一个子节点(相对简单)
- 该节点有两个子节点(情况复杂)
我们先从查找要删除的节点入手
- 先找到要删除的节点
- 找到要删除节点
- 删除叶子节点
- 删除只有一个子节点
- 删除有两个子节点的节点
typescript
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
left: TreeNode<T> | null = null
right: TreeNode<T> | null = null
parent: TreeNode<T> | null = null
get isLeft(): boolean {
return !!(this.parent && this.parent.left === this)
}
get isRight(): boolean {
return !!(this.parent && this.parent.right === this)
}
}
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
private searchNode(value: T): TreeNode<T> | null {
let current = this.root
let parent: TreeNode<T> | null = null
while (current) {
if (current.value === value) return current
parent = current
if (current.value < value) {
current = current.right
} else {
current = current.left
}
if (current) current.parent = parent
}
return null
}
}情况一:没有子节点
- 这种情况相对比较简单,我们需要检测 current 的 left 以及 right 是否都为 null
- 都为 null 之后还要检测一个东西,就是是否 current 就是根,都为 null,并且为根,那么相当于清空了根,因为只有它
- 否则就把父节点的 left 或者 right 字段设置为 null 即可
如果只有一个单独的根,直接删除即可
- 如果是叶节点,那么处理方式如下
typescript
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
remove(value: T): boolean {
// 1.搜索当前是否有这个value
const current = this.searchNode(value)
if (!current) return false
// 2.获取到三个东西:当前节点/父节点是否属于父节点的左子节点还是右子节点
// 2.1.如果删除的是叶子节点
if (current.left === null && current.right === null) {
if (current === this.root) {
// 根节点
this.root = null
} else if (current.isLeft) {
// 父节点的左子节点
current.parent!.left = null
} else {
current.parent!.right = null
}
}
return true
}
}情况二:一个子节点
- 这种情况也不是很难
- 要删除的 current 节点,只有 2 个连接(如果有两个子节点,就是三个连接了),一个连接父节点,一个连接唯一的子节点
- 需要从这三者之间:爷爷-自己-儿子,将自己(current)剪断,让爷爷直接连接儿子即可
- 这个过程要求改变父节点的 left 或者 right,指向要删除节点的子节点
- 当然,这个过程中还要考虑是否 current 就是根
js
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
remove(value: T): boolean {
if (current.right === null) {
// 2.2.只有一个子节点,只有左子节点
if (current === this.root) {
this.root = current.left
} else if (current.isLeft) {
current.parent!.left = current.left
} else {
current.parent!.right = current.left
}
} else if (current.left === null) {
// 2.3.只有一个子节点,只有右子节点
if (current === this.root) {
this.root = current.right
} else if (current.isLeft) {
current.parent!.left = current.right
} else {
current.parent!.right = current.right
}
}
return true
}
}情况三:两个节点

- 情况一:删除 9 节点
- 处理方式相对简单,将 8 位置替换到 9,或者将 10 位置替换到 9
- 注意:这里是替换,也就是 8 位置替换到 9 时,7 指向 8,而 8 还需要指向 10
- 找 8 或 10
- 情况二:删除 7 节点
- 一种方式是将 5 拿到 7 的位置,3 依然指向 5,但是 5 有一个 right,需要指向 9,依然是二叉搜索树
- 另一种方式是在右侧找一个,找 8
- 也就是将 8 替换到 7 的位置,8 的 left 指向 5,right 指向 9,依然是二叉搜索树
- 找 5 或 8
- 情况三:删除 15 节点,并且我希望也在右边找
- 18 替换 15 的位置,20 的 left 指向 19,也是一个二叉搜索树
- 找 14 或 18
typescript
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
private getSuccessor(delNode: TreeNode<T>) {
// 获取右子树
let current = delNode.right
let successor: TreeNode<T> | null = null
while (current) {
successor = current
current = current.left
if (current) {
current.parent = successor
}
}
// 拿到后继节点
if (successor !== delNode.right) {
successor!.parent!.left = successor!.right
successor!.right = delNode.right
}
// 将删除节点的 left,赋值给后继节点的 left
successor!.left = delNode.left
return successor
}
remove(value: T): boolean {
else {
// 2.4.两个子节点
const successor = this.getSuccessor(current)
if (current === this.root) {
this.root = successor
} else if (current.isLeft) {
current.parent!.left = successor
} else {
current.parent!.right = successor
}
}
return true
}
}寻找规律
如果我们要 删除的节点有两个子节点,甚至子节点还有子节点,这种情况下我们需要 从下面的子节点中找到一个子节点,来替换当前的节点
但是找到这个节点有什么特征呢?应该是 current 节点下面所有节点中 最接近 current 节点 的
- 要么比 current 节点小一点点,要么比 current 节点大一点点
- 总结你最接近 current,你就可以用来替换 current 的位置
这个节点怎么找呢?
- 比 current 小一点点的节点,一定是 current 左子树的最大值
- 比 current 大一点点的节点,一定是 current 右子树的最小值
前驱和后继
- 在二叉搜索树中,这两个特别的节点,有两个特别的名字
- 比 current 小一点点的节点,称为 current 节点的 前驱
- 比 current 大一点点的节点,称为 current 节点的 后继
也就是为了能够删除有两个子节点的 current,要么找到它的前驱,要么找到它的后继
typescript
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
remove(value: T): boolean {
// 1.搜索当前是否有这个value
const current = this.searchNode(value)
if (!current) return false
// 2.获取到三个东西:当前节点/父节点是否属于父节点的左子节点还是右子节点
let replaceNode: TreeNode<T> | null = null
if (current.left === null && current.right === null) {
// 2.1.如果删除的是叶子节点
replaceNode = null
} else if (current.right === null) {
// 2.2.只有一个子节点,只有左子节点
replaceNode = current.left
} else if (current.left === null) {
// 2.3.只有一个子节点,只有右子节点
replaceNode = current.right
} else {
// 2.4.两个子节点
const successor = this.getSuccessor(current)
replaceNode = successor
}
if (current === this.root) {
this.root = replaceNode
} else if (current.isLeft) {
current.parent!.left = replaceNode
} else {
current.parent!.right = replaceNode
}
return true
}
}删除操作非常复杂,一些程序员都尝试着避开删除操作
- 他们的做法是在 Node 类中添加一个 boolean 字段,比如名称为 isDeleted
- 要删除一个节点时,就将此字段设置为 true
- 其他操作,比如 find() 在查找之前先判断这个节点是不是标记为删除
- 这样相对比较简单,每次删除节点不会改变原有的树结构
- 但是在二叉树的存储中,还保留这那些本已经被删除掉的节点
二叉搜索树完整代码
typescript
import { btPrint } from 'hy-algokit'
class INode<T> {
value: T
constructor(value: T) {
this.value = value
}
}
class TreeNode<T> extends Node<T> {
left: TreeNode<T> | null = null
right: TreeNode<T> | null = null
parent: TreeNode<T> | null = null
get isLeft(): boolean {
return !!(this.parent && this.parent.left === this)
}
get isRight(): boolean {
return !!(this.parent && this.parent.right === this)
}
}
class BSTree<T> {
private root: TreeNode<T> | null = null
print() {
btPrint(this.root)
}
private searchNode(value: T): TreeNode<T> | null {
let current = this.root
let parent: TreeNode<T> | null = null
while (current) {
if (current.value === value) return current
parent = current
if (current.value < value) {
current = current.right
} else {
current = current.left
}
if (current) current.parent = parent
}
return null
}
/** 插入数据的操作 */
insert(value: T) {
// 1.根据传入value创建Node(TreeNode)节点
const newNode = new TreeNode(value)
// 2.判断当前是否已经有了根节点
if (!this.root) {
// 当前树为空
this.root = newNode
} else {
// 树中已经有其他值
this.insertNode(this.root, newNode)
}
}
private insertNode(node: TreeNode<T>, newNode: TreeNode<T>) {
if (newNode.value < node.value) {
// 去左边继续查找空白位置
if (node.left === null) {
node.left = newNode
} else {
this.insertNode(node.left, newNode)
}
} else {
// 去右边继续查找空白位置
if (node.right === null) {
node.right = newNode
} else {
this.insertNode(node.right, newNode)
}
}
}
// 遍历的操作
/** 先序遍历 */
preOrderTraverse() {
this.preOrderTraverseNode(this.root)
}
private preOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
console.log(node.value)
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.left)
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.right)
}
}
/** 中序遍历 */
inOrderTraverse() {
this.inOrderTraverseNode(this.root)
}
private inOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
this.inOrderTraverseNode(node.left)
console.log(node.value)
this.inOrderTraverseNode(node.right)
}
}
/** 后序遍历 */
postOrderTraverse() {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(this.root)
}
private postOrderTraverseNode(node: TreeNode<T> | null) {
if (node) {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(node.left)
this.postOrderTraverseNode(node.right)
console.log(node.value)
}
}
/** 层序遍历 */
levelOrderTraverse() {
// 1.如果没有根节点,那么不需要遍历
if (!this.root) return
// 2.创建队列结构
const queue: TreeNode<T>[] = []
queue.push(this.root)
// 3.遍历队列中所有的节点(依次出队)
while (queue.length) {
// 3.1访问节点的过程
const current = queue.shift()!
console.log(current.value)
// 3.2将左子节点放入队列
if (current.left) {
queue.push(current.left)
}
// 3.3将右子节点放入到队列
if (current.right) {
queue.push(current.right)
}
}
}
/** 获取最值操作:最大值 */
getMaxValue(): T | null {
let current = this.root
while (current && current.right) {
current = current.right
}
return current?.value ?? null
}
/** 获取最值操作:最小值 */
getMinValue(): T | null {
let current = this.root
while (current && current.left) {
current = current.left
}
return current?.value ?? null
}
/** 搜索特定的值 */
search(value: T): boolean {
return !!this.searchNode(value)
}
searchNodeValue(node: TreeNode<T> | null, value: T): boolean {
// 1.如果节点为null,那么就直接退出递归
if (node === null) return false
// 2.判断node节点的value和传入的value的大小
if (node.value > value) {
return this.searchNodeValue(node.left, value)
} else if (node.value < value) {
return this.searchNodeValue(node.right, value)
} else {
return true
}
}
/** 删除操作 */
private getSuccessor(delNode: TreeNode<T>) {
// 获取右子树
let current = delNode.right
let successor: TreeNode<T> | null = null
while (current) {
successor = current
current = current.left
if (current) {
current.parent = successor
}
}
// 拿到后继节点
if (successor !== delNode.right) {
successor!.parent!.left = successor!.right
successor!.right = delNode.right
}
// 将删除节点的 left,赋值给后继节点的 left
successor!.left = delNode.left
return successor
}
remove(value: T): boolean {
// 1.搜索当前是否有这个value
const current = this.searchNode(value)
if (!current) return false
// 2.获取到三个东西:当前节点/父节点是否属于父节点的左子节点还是右子节点
let replaceNode: TreeNode<T> | null = null
if (current.left === null && current.right === null) {
// 2.1.如果删除的是叶子节点
replaceNode = null
} else if (current.right === null) {
// 2.2.只有一个子节点,只有左子节点
replaceNode = current.left
} else if (current.left === null) {
// 2.3.只有一个子节点,只有右子节点
replaceNode = current.right
} else {
// 2.4.两个子节点
const successor = this.getSuccessor(current)
replaceNode = successor
}
if (current === this.root) {
this.root = replaceNode
} else if (current.isLeft) {
current.parent!.left = replaceNode
} else {
current.parent!.right = replaceNode
}
return true
}
}自动补全和搜索建议
常用的数据结构包括前缀树(Trie)和哈希表
- 前缀树用于存储和快速查找具有相同前缀的单词,适用于实现搜索建议的自动补全功能
- 哈希表则常用于存储搜索建议的数据源,提供快速的检索和访问
字符串比较是按照字典次序对单个字符或字符串进行比较大小的操作,一般都是以 ASCII 码值的大小作为字符比较的标准。对两个字符串进行比较时,要注意以下几点:
- 两个不同长度的字符串进行比较时,不是唱的字符串就一定大。比如:
abcd与acd比较,第一个字符相同,继续比较第二个字符,由于c > b,所以不再继续比较,结果就是acd大 - 当字符串有空格时,空格也参加比较。比如:
c at与cat比较,空格的 ASCII 码是 32,a 的 ASCII 码是 97,所以cat > c at - 大小写字母的 ASCII 码值是有区别的。比如:A 的 ASCII 码是 64,a 的 ASCII 码是 97,所以
angle > Angle
html
<body>
<input type="text" id="searchInput" placeholder="Search" />
<div id="suggestions"></div>
</body>
<script>
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value
this.left = null
this.right = null
}
}
class BST {
constructor() {
this.root = null
}
insert(value) {
const newNode = new Node(value)
if (!this.root) {
this.root = newNode
} else {
this.insertNode(this.root, newNode)
}
}
insertNode(node, newNode) {
if (newNode.value < node.value) {
if (!node.left) {
node.left = newNode
} else {
this.insertNode(node.left, newNode)
}
} else {
if (!node.right) {
node.right = newNode
} else {
this.insertNode(node.right, newNode)
}
}
}
searchSuggestions(prefix) {
let suggestions = []
this.searchNode(this.root, prefix, suggestions)
return suggestions
}
searchNode(node, prefix, suggestions) {
if (!node) return
if (node.value.startsWith(prefix)) {
suggestions.push(node.value)
}
if (prefix < node.value) {
this.searchNode(node.left, prefix, suggestions)
} else {
this.searchNode(node.right, prefix, suggestions)
}
}
}
const bst = new BST()
bst.insert('banana')
bst.insert('apple')
bst.insert('grape')
bst.insert('orange')
bst.insert('cherry')
const searchInput = document.getElementById('searchInput')
const suggestionsElement = document.getElementById('suggestions')
searchInput.addEventListener('input', () => {
const prefix = searchInput.value
const suggestions = bst.searchSuggestions(prefix)
suggestionsElement.innerHTML = ''
suggestions.forEach(suggestion => {
const suggestionDiv = document.createElement('div')
suggestionDiv.textContent = suggestion
suggestionsElement.appendChild(suggestionDiv)
})
})
</script>